In a page report or a RDL report, you can use custom code in your expressions to extend the capabilities of your report. However, for complex functions, or functions you plan to use many times in the report, you also have the facility to embed the code within the report. You can also create and maintain a custom assembly for code that you want to use in multiple reports and refer to its methods in expressions.
Embed Code in the Report
Add a page report/RDL report template to your project and in the ActiveReports Designer that appears, add code like the following in the Script tab.

To call a function from the control's property
This is a simple example of a single method code block:
Public Function GetDueDate() as Date
Return DateTime.Now.AddDays(30)
End Function
This is an expression used to call the method in the code block from the control's property. For example, you can call this function in the Value property of the Textbox control:
=Code.GetDueDate()
To use the custom constant and variable from the control's property
This is a simple example of how to define custom constants and variables in your code block:
Public Dim MyVersion As String = "123.456"
Public Dim MyDoubleVersion As Double = 123.456
Public Const MyConst As String = "444"
This is an expression to use the custom constant and variable in the code block from the control's property. For example, you can get the value of a variable or a constant in the Value property of the Textbox control:
=Code.MyVersion
=Code.MyDoubleVersion
=Code.MyConst
To call a global collection from the control's property
This is a simple example of a global collection code block where the code block references the report object to access the report parameter value:
Public Function ReturnParam() As String
Return "param value = " + Report.Parameters!ReportParameter1.value.ToString()
End Function
This is an expression used to call a global collection in the code block from the control's property. For example, you can call the global collection in the Value property of the Textbox control:
=Code.ReturnParam()
Use instance-based Visual Basic .NET code in the form of a code block. You can include multiple methods in your code block, and access those methods from expressions in the control properties.
 |
Note: In a page report or a RDL report, you can use Visual Basic.NET as the script language. However, you can use both Visual Basic.Net and C# in your script for a section report. |
Create custom assemblies
You can create custom assemblies in C# or Visual Basic .NET to make code available to multiple reports:
- Create or find the assembly you wish to use.
- Make the assembly available to the report engine.
- If you are embedding the designer or viewer controls in your own application, copy the assembly to the same location as your executable.
- If you are using the included designer or viewer, copy the assembly into the ActiveReports assembly folder located at ...\Common Files\ComponentOne\ActiveReports 9 by default.
Note: To make the assembly available for use in your own application and for use in designing reports for your application, copy it to both locations listed above. Alternatively, you can place the assembly in the Global Assembly Cache (C:\Windows\assembly).
- Add an assembly reference to the report.
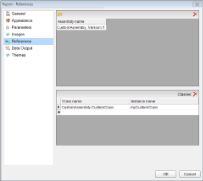
- From the Report Menu, choose Report Properties.
- In the Report dialog that appears, select the References and click the Open icon above the assembly name list to add your own assembly.
- Go to the Class list below the assembly names and under Class name, enter the namespace and class name. Similarly, under Instance name, enter the name you want to use in your expressions.
- Access the assembly through expressions.
- To access static members (member denoted as
public staticin C# assemblies, or asPublic Sharedin Visual Basic assemblies):
=Namespace.Class.Member - To access class instances:
=Code.InstanceName
- To access static members (member denoted as
 Show All
Show All Hide All
Hide All