The following code provides an example of how to format the cells of a book.
1. Add a reference to C1.Silverlight.Excel.dlland create a C1XLBook.
2. Add code to format the cells.
3. Save the workbook. The code looks like the following. In this example it is placed within a button1_Click event so the Save As dialog box will open when the user clicks the button
•C#
private void button1_Click_1(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// create a new workbook to be saved
SaveBook(book =>
{
XLSheet sheet = book.Sheets[0];
// create a style
XLStyle totalStyle = new XLStyle(book);
totalStyle.Font = new XLFont("Arial", 12, true, false);
// create an outline and apply styles
sheet[2, 1].Value = "Number";
sheet[2, 2].Value = "ID";
sheet[3, 1].Value = 12;
sheet[3, 2].Value = 17;
sheet.Rows[3].OutlineLevel = 2;
sheet.Rows[3].Visible = false;
sheet[4, 1].Value = 12;
sheet[4, 2].Value = 14;
sheet.Rows[4].OutlineLevel = 2;
sheet.Rows[4].Visible = false;
sheet[5, 1].Value = "12 Total";
sheet[5, 1].Style = totalStyle;
sheet[5, 2].Value = 31;
sheet[5, 2].Formula = "SUBTOTAL(9,C4:C5)";
sheet.Rows[5].OutlineLevel = 1;
sheet[6, 1].Value = 34;
sheet[6, 2].Value = 109;
sheet.Rows[6].OutlineLevel = 2;
sheet[7, 1].Value = "34 Total";
sheet[7, 1].Style = totalStyle;
sheet[7, 2].Value = 109;
sheet[7, 2].Formula = "SUBTOTAL(9,C7:C7)";
sheet.Rows[7].OutlineLevel = 1;
sheet[8, 1].Value = "Grand Total";
sheet[8, 1].Style = totalStyle;
sheet[8, 2].Value = 140;
sheet[8, 2].Formula = "SUBTOTAL(9,C4:C7)";
sheet.Rows[8].OutlineLevel = 0;
});
}
// save the file
private void SaveBook(Action<C1XLBook> action)
{
var dlg = new SaveFileDialog();
dlg.Filter = "Excel Files (*.xlsx)|*.xlsx";
if (dlg.ShowDialog() == true)
{
try
{
var book = new C1XLBook();
if (action != null)
{
action(book);
}
using (var stream = dlg.OpenFile())
{
book.Save(stream);
}
}
catch (Exception x)
{
MessageBox.Show(x.Message);
}
}
}
4.
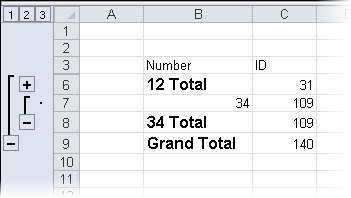
Run the program. Save and open the file. The spreadsheet will look similar to
the following:
The SUBTOTAL formulas get the sum of the specified rows.