Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a design pattern used by applications that require multiple views of the same data. The MVC pattern requires the separation of individual objects into three categories depicted in the following diagram:
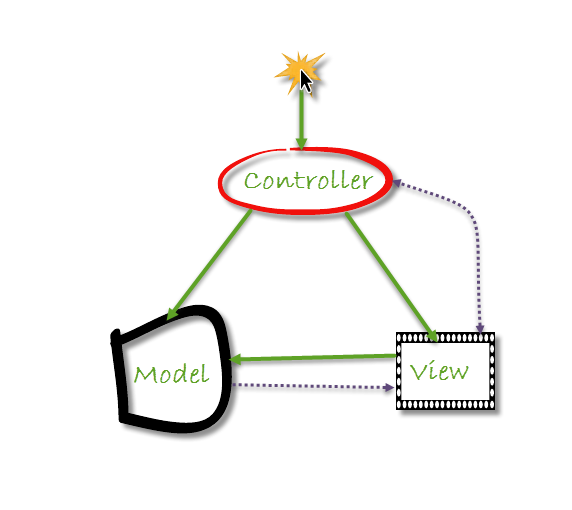
Controllers: Classes that handle incoming requests to the application, retrieve model data, and then specify view templates that return a response to the client.
Models: Classes that represent the data of the application and that use validation logic to enforce business rules for that data.
Views: Template files that your application uses to dynamically generate HTML responses. Helper methods, such as HTML Helpers and Tag Helpers, simplify the generation of these HTML responses.
The control flow in an MVC application would be as follows:
- Someone interacts with the UI in a way that triggers an event.
- The controller notifies the model of the user’s interaction and requests an action.
- Model performs the requested action.
- The controller requests for the view to display the result of the action.
- The view (or views) query the model to generate the new view and grabs the data from the model.
- The view displays the results.