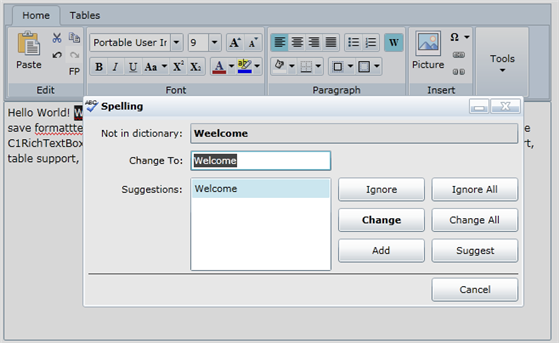
Modal Spell-Checking
To implement modal spell checking, you start by adding to your project a reference to the C1.Silverlight.SpellChecker assembly. Then, add the following code to your project:
Imports C1.Silverlight.SpellChecker
Public Partial Class MainPage
Inherits UserControl
' Spell-checker used by all controls on this page
Private _spell As New C1SpellChecker()
' Page constructor
Public Sub New()
' Regular Standard initialization
InitializeComponent()
' Load main spelling dictionary
AddHandler _spell.MainDictionary.LoadCompleted, AddressOf MainDictionary_LoadCompleted
_spell.MainDictionary.LoadAsync("C1Spell_en-US.dct")
' Load user dictionary
Dim ud As UserDictionary = _spell.UserDictionary
ud.LoadFromIsolatedStorage("Custom.dct")
' Other initializations
' ...
AddHandler App.Current.[Exit], AddressOf App_Exit
End Sub
End Class
•C#
using C1.Silverlight.SpellChecker;
public partial class MainPage : UserControl
{
// Spell-checker used by all controls on this page
C1SpellChecker _spell = new C1SpellChecker();
// Page constructor
public MainPage()
{
// Standard initialization
InitializeComponent();
// Load main spelling dictionary
_spell.MainDictionary.LoadCompleted += MainDictionary_LoadCompleted;
_spell.MainDictionary.LoadAsync("C1Spell_en-US.dct");
// Load user dictionary
UserDictionary ud = _spell.UserDictionary;
ud.LoadFromIsolatedStorage("Custom.dct");
App.Current.Exit += App_Exit;
// Other initializations
// ...
}
}
The code creates a new C1SpellChecker object to be shared by all controls on the page that require spell-checking.
Later, the page constructor invokes the LoadAsync method to load the main spell dictionary. In this case, we are loading C1Spell_en-US.dct, the American English dictionary. This file must be present on the application folder on the server. C1SpellChecker includes over 20 other dictionaries which can be downloaded from our site.
The code adds a handler to the SpellDictionaryBase.LoadCompleted event so it can detect when the main dictionary finishes loading and whether there were any errors. Here is a typical event handler:
Private Sub MainDictionary_LoadCompleted(sender As Object, e As OpenReadCompletedEventArgs)
If e.[Error] IsNot Nothing Then
MessageBox.Show("Error loading spell dictionary, " & "spell-checking is disabled.")
End If
End Sub
•C#
void MainDictionary_LoadCompleted(object sender, OpenReadCompletedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Error != null)
MessageBox.Show("Error loading spell dictionary, " +
"spell-checking is disabled.");
}
The code also loads a user dictionary from isolated storage. This step is optional. The user dictionary stores words such as names and technical terms. The code attaches an event handler to the application's Exit event to save the user dictionary when the application finishes executing:
Private Sub App_Exit(sender As Object, e As EventArgs)
Dim ud As UserDictionary = _spell.UserDictionary
ud.SaveToIsolatedStorage("Custom.dct")
End Sub
•C#
void App_Exit(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
UserDictionary ud = _spell.UserDictionary;
ud.SaveToIsolatedStorage("Custom.dct");
}
Once the dictionary has been loaded, you can invoke the modal spell-checker by calling the C1SpellChecker.CheckControlAsync method. For example:
Private Sub SpellCheck_Click(sender As Object, e As RoutedEventArgs)
AddHandler _spell.CheckControlCompleted, AddressOf _spell_CheckControlCompleted
_spell.CheckControlAsync(_rtb)
End Sub
Private Sub _spell_CheckControlCompleted(sender As Object, e As CheckControlCompletedEventArgs)
If Not e.Cancelled Then
Dim msg = String.Format("Spell-check complete. {0} error(s) found.", e.ErrorCount)
MessageBox.Show(msg, "Spell-check complete", MessageBoxButton.OK)
End If
End Sub
•C#
private void SpellCheck_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
_spell.CheckControlCompleted += _spell_CheckControlCompleted;
_spell.CheckControlAsync(_rtb);
}
void _spell_CheckControlCompleted(object sender, CheckControlCompletedEventArgs e)
{
if (!e.Cancelled)
{
var msg = string.Format(
"Spell-check complete. {0} error(s) found.", e.ErrorCount);
MessageBox.Show(msg, "Spell-check complete..", MessageBoxButton.OK);
}
}
The code calls C1SpellChecker.CheckControlAsync. When the modal checking is complete, the C1SpellChecker.CheckControlCompleted event fires and shows a dialog box to indicate that the spell-checking operation is complete.
The image below shows the spell-checking dialog box in action:
