Double-click the first textbox and add the following code to the TextBox1_GotFocus event:
Private Sub TextBox1_GotFocus(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles TextBox1.GotFocus
C1Spell1.CheckTyping(TextBox1)
C1Spell1.IntegerTag = 1
End Sub
• C#
private void textBox1_GotFocus(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
c1Spell1.CheckTyping(textBox1);
c1Spell1.IntegerTag = 1;
}
Add the following code to the TextBox2_GotFocus and TextBox3_GotFocus events, respectively.
Private Sub TextBox2_GotFocus(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles TextBox2.GotFocus
C1Spell1.CheckTyping(TextBox2)
C1Spell1.IntegerTag = 2
End Sub
Private Sub TextBox3_GotFocus(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles TextBox3.GotFocus
C1Spell1.CheckTyping(TextBox3)
C1Spell1.IntegerTag = 3
End Sub
• C#
private void textBox2_GotFocus(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
c1Spell1.CheckTyping(textBox2);
c1Spell1.IntegerTag = 2;
}
private void textBox3_GotFocus(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
c1Spell1.CheckTyping(textBox3);
c1Spell1.IntegerTag = 3;
}
The code starts by connecting the C1Spell component to the textbox that has the focus. Then the CheckTyping method is used for basic as-you-type spell checking. The value of the current textbox is then saved into the C1Spell.IntegerTag property.
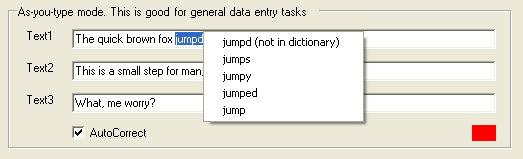
By default, the C1Spell component will beep and underline misspelled words. Our demo will provide additional functionality. We will show a red sign when a bad word is detected and, optionally, display a list of suggestions. To do this, add the following code to the C1Spell1.TypingError event:
Private Sub C1Spell1_TypingError(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As C1.Win.C1Spell.TypingErrorEventArgs) Handles C1Spell1.TypingError
' show red light to indicate an error was detected
PictureBox1.BackColor = Color.Red
' if AutoCorrect is not set, we are done
If Not CheckBox1.Checked Then
C1Spell1.TypingErrorAction = C1.Win.C1Spell.TypingErrorActionEnum.Underline
Exit Sub
End If
C1Spell1.TypingErrorAction = C1.Win.C1Spell.TypingErrorActionEnum.NoAction
' use CheckString method to build a list of suggestions
C1Spell1.CheckString(e.ErrWord, C1.Win.C1Spell.BadWordDialogEnum.NoDialog)
' if no suggestions, just quit
If C1Spell1.Suggestions.Count = 0 Then Exit Sub
' now select the word
SetSelection(e.SelStart, e.SelLength)
' only one suggestion, assume it is the correct word
' replace it automatically
If C1Spell1.Suggestions.Count = 1 Then
ChangeText(C1Spell1.Suggestions(0))
Exit Sub
End If
' build the context menu if there are at least two
' suggestions and put the suggestion words as the menu texts
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 5
Me.ContextMenuStrip1.MenuItems(i).Visible = False
Next
Me.ContextMenuStrip1.MenuItems(0).Text = e.ErrWord & " (not in dictionary)"
For i = 1 To 5
If i > 5 Then Exit For
If C1Spell1.Suggestions.Count < i Then Exit For
Me.ContextMenuStrip1.MenuItems(i).Text = C1Spell1.Suggestions(i - 1)
Me.ContextMenuStrip1.MenuItems(i).Visible = True
Next
' Show the context menu at the current caret position
' note that the caret position is the screen position and it
' should be transferred to the client position for each
' textbox
Dim pos As Point
Dim x, y
x = C1Spell1.CaretPosX
y = C1Spell1.CaretPosY
pos = New Point(x, y)
Select Case C1Spell1.IntegerTag
Case 1
pos = TextBox1.PointToClient(pos)
Me.ContextMenuStrip1.Show(TextBox1, pos)
Case 2
pos = TextBox2.PointToClient(pos)
Me.ContextMenuStrip1.Show(TextBox2, pos)
Case 3
pos = TextBox3.PointToClient(pos)
Me.ContextMenuStrip1.Show(TextBox3, pos)
End Select
End Sub
'this sub routine will select the error word
Private Sub SetSelection(ByVal start, ByVal length)
Select Case C1Spell1.IntegerTag
Case 1
TextBox1.Select(start, length)
Case 2
TextBox2.Select(start, length)
Case 3
TextBox3.Select(start, length)
End Select
End Sub
• C#
private void c1Spell1_TypingError( object sender, C1.Win.C1Spell.TypingErrorEventArgs e)
{
// show red light to indicate an error was detected
pictureBox1.BackColor = Color.Red;
// if AutoCorrect is not set, we are done
if (! checkBox1.Checked )
{
c1Spell1.TypingErrorAction = C1.Win.C1Spell.TypingErrorActionEnum.Underline;
return;
}
c1Spell1.TypingErrorAction = C1.Win.C1Spell.TypingErrorActionEnum.NoAction;
// use CheckString method to build a list of suggestions
c1Spell1.CheckString(e.ErrWord, C1.Win.C1Spell.BadWordDialogEnum.NoDialog);
// if no suggestions, just quit
if ( c1Spell1.Suggestions.Count == 0 ) return;
// now select the word
SetSelection(e.SelStart, e.SelLength);
// only one suggestion, assume it is the correct word
// replace it automatically
if ( c1Spell1.Suggestions.Count == 1 )
{
ChangeText(c1Spell1.Suggestions[0]);
return;
}
// build the context menu if there are at least two
// suggestions and put the suggestion words as the menu texts
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
this.contextMenuStrip1.MenuItems[i].Visible = false;
this.contextMenuStrip1.MenuItems[0].Text = e.ErrWord + " (not in dictionary)";
for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
if ( c1Spell1.Suggestions.Count < i ) break;
this.contextMenuStrip1p.MenuItems[i].Text = c1Spell1.Suggestions[i - 1];
this.contextMenuStrip1.MenuItems[i].Visible = true;
}
// Show the context menu at the current caret position
// note that the caret position is the screen position and it
// should be transferred to the client position for each
// textbox
Point pos;
int x, y;
x = c1Spell1.CaretPosX;
y = c1Spell1.CaretPosY;
pos = new Point(x, y);
switch (c1Spell1.IntegerTag)
{
case 1:
pos = textBox1.PointToClient(pos);
this.contextMenuStrip1.Show(TextBox1, pos);
case 2:
pos = textBox2.PointToClient(pos);
this.contextMenuStrip1.Show(TextBox2, pos);
case 3:
pos = textBox3.PointToClient(pos);
this.contextMenuStrip1.Show(TextBox3, pos);
}
}
// this sub routine will select the error word
private void SetSelection( start, length)
{
switch (c1Spell1.IntegerTag)
{
case 1:
textBox1.Select(start, length);
case 2:
textBox2.Select(start, length);
case 3:
textBox3.Select(start, length);
}
}
This routine is pretty long, but it's fairly simple. The routine works as follows:
• If the AutoCorrect option is off, it simply shows the red shape to indicate that a word was misspelled and allows the C1Spell1 component to provide the default user-feedback actions (beep and underline the offending word).
• If AutoCorrect is on, the routine uses the C1Spell1 CheckString method to build a list of suggestions.
• If C1Spell cannot provide any suggestions, the routine returns immediately.
• If a single suggestion is provided, the code replaces the offending word with the suggestion automatically. This is probably not a great idea in practice, but it's interesting to watch as the component corrects words automatically.
• Finally, if many suggestions are available, the component assembles them into a pop-up menu and prompts the user to select one of the options. In the demo, we only use the first five suggestions.
To make the pop-up menu work, we need to implement the menu-handling and text-changing functions. This code allows the user to select one of the items from the pop-up menu to replace the misspelled word. Once an error is corrected, the PictureBox will become green.
Private Sub MenuItem1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MenuItem1.Click
' Ignore this word
Me.C1Spell1.IgnoreAllWord = True
' change the color
PictureBox1.BackColor = Color.Green
End Sub
' this sub routine will change the error word to
' val
Private Sub ChangeText(ByVal val As String)
Dim subStr As String
Select Case C1Spell1.IntegerTag
Case 1
TextBox1.SelectedText = val
Case 2
TextBox2.SelectedText = val
Case 3
TextBox3.SelectedText = val
End Select
' the error is corrected
PictureBox1.BackColor = Color.Green
End Sub
Private Sub MenuItem2_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MenuItem2.Click
' handle menu click
ChangeText(MenuItem2.Text)
End Sub
Private Sub MenuItem3_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MenuItem3.Click
' handle menu click
ChangeText(MenuItem3.Text)
End Sub
Private Sub MenuItem4_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MenuItem4.Click
' handle menu click
ChangeText(MenuItem4.Text)
End Sub
Private Sub MenuItem5_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MenuItem5.Click
' handle menu click
ChangeText(MenuItem5.Text)
End Sub
Private Sub MenuItem6_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MenuItem6.Click
' handle menu click
ChangeText(MenuItem6.Text)
End Sub
• C#
private void menuItem1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Ignore this word
this.c1Spell1.IgnoreAllWord = true;
// change the color
pictureBox1.BackColor = Color.Green;
}
// this sub routine will change the error word to
// val
private void ChangeText(string val)
{
string subStr;
switch (c1Spell1.IntegerTag)
{
case 1:
textBox1.SelectedText = val;
case 2:
textBox2.SelectedText = val;
case 3:
textBox3.SelectedText = val;
}
// the error is corrected
pictureBox1.BackColor = Color.Green;
}
private void menuItem2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// handle menu click
ChangeText(menuItem2.Text);
}
private void menuItem3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// handle menu click
ChangeText(menuItem3.Text);
}
private void menuItem4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// handle menu click
ChangeText(menuItem4.Text);
}
private void menuItem5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// handle menu click
ChangeText(menuItem5.Text);
}
private void menuItem6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// handle menu click
ChangeText(menuItem6.Text);
}
We're almost done now. We need to be able to hide the red shape when the user types in a word that is correct. This can be done easily using the C1Spell1.TypingOK event.
Private Sub C1Spell1_TypingOK(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As C1.Win.C1Spell.TypingOKEventArgs) Handles C1Spell1.TypingOK
' typed something right? Use green color.
PictureBox1.BackColor = Color.Green
End Sub
• C#
private void c1Spell1_TypingOK(object sender, C1.Win.C1Spell.TypingOKEventArgs e)
{
// typed something right? Use green color.
pictureBox1.BackColor = Color.Green;
}
That's it for the top pane on our demo. Save the project and run it. Start typing into the top three textboxes and you will see as-you-type spell checking in action.
Here's how the main form looks when an error is found:
|
