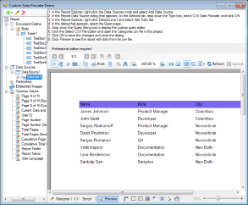
A custom data provider allows you to use non-traditional data sources in your page reports, both at run time and at design time. This walkthrough illustrates how to create a solution with projects that create a custom data provider and demonstrate how it pulls data from a comma separated values (CSV) file.
This walkthrough is split into the following activities:
- Creating a Designer project to demonstrate the custom data provider
- Configuring the project to use a custom data provider
- Adding a report to show the data
- Adding a second project to contain the custom data provider
- Adding a button to the query editor
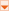
When you complete this walkthrough, you will have a designer pre-loaded with a report that pulls data from a CSV file and looks like the following.
 To create a Designer project to demonstrate the custom data provider
To create a Designer project to demonstrate the custom data provider
- In Visual Studio, create a Windows Forms project and name it CustomDataProviderDemo.
- From the Visual Studio toolbox ActiveReports 7 tab, drag a ReportExplorer and drop it onto the default Windows form, resizing the form to a comfortable working area.
- In the Properties window, set the Dock property of the ReportExplorer control to Left.
- From the toolbox Common Controls tab, drag a RichTextBox control onto the form and set the Dock property to Top.
- Add the following text to the Text property. (Drop down the box to ensure that all of the lines of text are added.)
Text. Paste in the Text property of the RichTextBox.  Copy Code
Copy Code1. In the Report Explorer, right-click the Data Sources node and select Add Data Source. 2. In the Report Data Source dialog that appears, on the General tab, drop down the Type box, select CSV Data Provider, and click OK. 3. In the Report Explorer, right-click DataSource1 and select Add Data Set. 4. In the dialog that appears, select the Query page. 5. Drop down the Query String box to display the custom query editor. 6. Click the Select CSV File button and open the Categories.csv file in this project. 7. Click OK to save the changes and close the dialog. 8. Click Preview to see the report with data from the csv file.
- From the toolbox ActiveReports 7 tab, drag a Designer control and drop it on the empty part of the form.
- Set the Dock property to Fill, then right-click the Designer control on the form and select Bring to front.
- Select the ReportExplorer control and in the Properties window, drop down the ReportDesigner property and select Designer1.
- Double-click on the form's title bar to create a form Load event, and add code like the following above the class.
Visual Basic code. Paste above the class.  Copy Code
Copy CodeImports System.Xml Imports System.IO Imports GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Design
C# code. Paste above the class.  Copy Code
Copy Codeusing System.Xml; using System.IO; using GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Design;
- Add the following code to the form Load event.
Visual Basic code. Paste inside the form Load event.  Copy Code
Copy CodeUsing reportStream = File.OpenRead("DemoReport.rdlx") Using reader = XmlReader.Create(reportStream) Designer1.LoadReport(reader, DesignerReportType.Page) End Using End UsingC# code. Paste inside the form Load event.  Copy Code
Copy Codeusing (var reportStream = File.OpenRead("DemoReport.rdlx")) { using (var reader = XmlReader.Create(reportStream)) { designer1.LoadReport(reader, DesignerReportType.Page); } }
 To configure the project to use a custom data provider
To configure the project to use a custom data provider
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click the project and select Add, then New Item.
- In the dialog that appears, select Text File, name it GrapeCity.ActiveReports.config, and click Add.
- In the Solution Explorer, select the new file and in the Properties window, set its Copy to Output Directory property to Copy always.
- Paste the following text into the file and save it. (You can safely ignore the warning that the 'Configuration' element is not declared.)
Paste into the config file.  Copy Code
Copy Code<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <Configuration> <Extensions> <Data> <Extension Name="CSV" DisplayName="CSV Data Provider" Type="CustomDataProvider.CsvDataProvider.CsvDataProviderFactory, CustomDataProvider" CommandTextEditorType="CustomDataProvider.CSVDataProvider.QueryEditor, CustomDataProvider"/> </Data> </Extensions> </Configuration> - In the Solution Explorer, right-click the project and select Add, then New Item.
- In the dialog that appears, select Text File, name it Categories.csv, and click Add.
- In the Solution Explorer, click to select the file, and in the Properties window, change the Copy to Output Directory property to Copy always.
- Paste the following text into the file and save it.
Paste into the text file.  Copy Code
Copy CodeEmployeeID(int32),LastName,FirstName,Role,City 1,James,Yolanda,Owner,Columbus 7,Reed,Marvin,Manager,Newton 9,Figg,Murray,Cashier,Columbus 12,Snead,Lance,Store Keeper,Columbus 15,Halm,Jeffry,Store Keeper,Columbus 17,Hames,Alma,Store Keeper,Oak Bay 18,Nicki,Aubrey,Store Keeper,Columbus 24,Cliett,Vikki,Store Keeper,Newton
 To add a report to show the data from the custom data provider
To add a report to show the data from the custom data provider
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click the project and select Add, then New Item.
- In the dialog that appears, select ActiveReports 7 Page Report, name it DemoReport, and click Add.
- In the Solution Explorer, click to select the report, and in the Properties window, change the Copy to Output Directory property to Copy always.
- Click on the report design surface to show the Report menu, drop down that menu, and select Convert to CPL report. (This way all of our data shows on one page.)
- From the ActiveReports 7 Page Report Toolbox, drag a Table report control onto the report.
Note: In case you are still working on FPL layout, set the FixedSize property of the Table control to display all data on one page. - Click inside the table to reveal the table adorners, then right-click the table adorner to the left of the footer row and select Delete Rows. The footer row is removed from the table.
- In the Report Explorer, select each of the textboxes in turn and set the properties as in the following table. (If you do not see the Report Explorer, from the View menu, select Other Windows, then Report Explorer 7.)
TextBox Name Value Property BackgroundColor Property TextBox1 Name MediumSlateBlue TextBox2 Role MediumSlateBlue TextBox3 City MediumSlateBlue TextBox4 =Fields!FirstName.Value & " " & Fields!LastName.Value TextBox5 =Fields!Role.Value TextBox6 =Fields!City.Value - In the Report Explorer, select the Table1 node and in the Properties window, set the Location property to 1in, 1in and the Size property to 6in, 0.5in to make the table wide enough to see all of the data.
- With Table1 still selected in the Properties window, in the DataSetName property, enter the text DataSet1.
 To add a class library project to the solution to contain the custom data provider
To add a class library project to the solution to contain the custom data provider
- From the File menu, select Add, then New Project.
- In the Add New Project dialog, select Class Library, and name the project CustomDataProvider.
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click the default class and select Delete. (We will add our classes to a folder below.)
- Right-click the CustomDataProvider project and select Add Reference, and in the Add Reference dialog that appears, on the .NET tab, select the following references to add, holding down the Ctrl button to select multiple references.
- GrapeCity ActiveReports Developer 7 (GrapeCity.ActiveReports.v7)
- GrapeCity ActiveReports Extensibility Library (GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.v7)
- System.Drawing
- System.Windows.Forms
- Right-click the CustomDataProvider project and select Add, then New Folder, and name the folder CSVDataProvider.
- Right-click the folder and select Add, then Class, then name the class CsvColumn and add code like the following to replace the default stub in the class.
Visual Basic code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy CodeNamespace CSVDataProvider ' Represents information about fields in the data source. Friend Structure CsvColumn Private ReadOnly _fieldName As String Private ReadOnly _dataType As Type ' Creates a new instance of the CsvColumn class. ' The fieldName parameter is the name of the field represented by this instance of the CsvColumn. ' The dataType parameter is the Type of the field represented by this instance of the CsvColumn. Public Sub New(fieldName As String, dataType As Type) If fieldName Is Nothing Then Throw New ArgumentNullException("fieldName") End If If dataType Is Nothing Then Throw New ArgumentNullException("dataType") End If _fieldName = fieldName _dataType = dataType End Sub ' Gets the name of the field represented by this instance of the CsvColumn. Public ReadOnly Property FieldName() As String Get Return _fieldName End Get End Property ' Gets the the Type of the field represented by this instance of the CsvColumn. Public ReadOnly Property DataType() As Type Get Return _dataType End Get End Property ' Returns a String that represents this instance of the CsvColumn. Public Overrides Function ToString() As String Return [String].Concat(New String() {FieldName, "(", DataType.ToString(), ")"}) End Function ' Determines whether two CsvColumn instances are equal. ' The obj represents the CsvColumn to compare with the current CsvColumn. ' Returns True if the specified CsvColumn is equal to the current CsvColumn; otherwise, False. Public Overrides Function Equals(obj As Object) As Boolean Dim flag As Boolean If TypeOf obj Is CsvColumn Then flag = Equals(CType(obj, CsvColumn)) Else flag = False End If Return flag End Function Private Overloads Function Equals(column As CsvColumn) As Boolean Return column.FieldName = FieldName End Function ' Serves as a hash function for a CsvColumn, suitable for use in hashing algorithms and data structures like a hash table. ' Returns a hash code for the current CsvColumn instance. Public Overrides Function GetHashCode() As Integer Return (FieldName.GetHashCode() + DataType.GetHashCode()) End Function End Structure End NamespaceC# code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy Codeusing System; namespace CustomDataProvider.CSVDataProvider { // Represents information about fields in the data source. internal struct CsvColumn { private readonly string _fieldName; private readonly Type _dataType; // Creates a new instance of the CsvColumn class. // The fieldName parameter is the name of the field represented by this instance of the CsvColumn. // The dataType parameter is the Type of the field represented by this instance of the CsvColumn. public CsvColumn(string fieldName, Type dataType) { if (fieldName == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("fieldName"); if (dataType == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("dataType"); _fieldName = fieldName; _dataType = dataType; } // Gets the name of the field represented by this instance of the CsvColumn. public string FieldName { get { return _fieldName; } } // Gets the the Type of the field represented by this instance of the CsvColumn. public Type DataType { get { return _dataType; } } // Returns a String that represents this instance of the CsvColumn. public override string ToString() { return String.Concat(new string[] {FieldName, "(", DataType.ToString(), ")"}); } // Determines whether two CsvColumn instances are equal. // The obj represents the CsvColumn to compare with the current CsvColumn. // Returns True if the specified CsvColumn is equal to the current CsvColumn; otherwise, False. public override bool Equals(object obj) { bool flag; if (obj is CsvColumn) { flag = Equals((CsvColumn) obj); } else { flag = false; } return flag; } private bool Equals(CsvColumn column) { return column.FieldName == FieldName; } // Serves as a hash function for a CsvColumn, suitable for use in hashing algorithms and data structures like a hash table. // Returns a hash code for the current CsvColumn instance. public override int GetHashCode() { return (FieldName.GetHashCode() + DataType.GetHashCode()); } } } - Right-click the CSVDataProvider folder and select Add, then Class, then name the class CsvDataReader and add code like the following to replace the default stub in the class.
Visual Basic code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy CodeImports System Imports System.Collections Imports System.Globalization Imports System.IO Imports System.Text.RegularExpressions Imports GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.Data Namespace CSVDataProvider ' Provides an implementation of IDataReader for the .NET Framework CSV Data Provider. Friend Class CsvDataReader Implements IDataReader 'NOTE: HashcodeProvider and Comparer need to be case-insensitive since TypeNames are capitalized differently in places. 'Otherwise data types end up as strings when using Int32 vs int32. Private _typeLookup As New Hashtable(StringComparer.Create(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, False)) Private _columnLookup As New Hashtable() Private _columns As Object() Private _textReader As TextReader Private _currentRow As Object() 'The regular expressions are set to be pre-compiled to make it faster. Since we were concerned about 'multi-threading, we made the properties read-only so no one can change any properties on these objects. Private Shared ReadOnly _rxDataRow As New Regex(",(?=(?:[^""]*""[^""]*"")*(?![^""]*""))", RegexOptions.Compiled) 'Used to parse the data rows. Private Shared ReadOnly _rxHeaderRow As New Regex("(?<fieldName>(\w*\s*)*)\((?<fieldType>\w*)\)", RegexOptions.Compiled) 'Used to parse the header rows. ' Creates a new instance of the CsvDataReader class. ' The textReader parameter represents the TextReader to use to read the data. Public Sub New(textReader As TextReader) _textReader = textReader ParseCommandText() End Sub ' Parses the passed-in command text. Private Sub ParseCommandText() If _textReader.Peek() = -1 Then Return End If 'Command text is empty or at the end already. FillTypeLookup() Dim header As String = _textReader.ReadLine() header = AddDefaultTypeToHeader(header) If Not ParseHeader(header) Then Throw New InvalidOperationException( _ "Field names and types are not defined. " & _ "The first line in the CommandText must contain the field names and data types. e.g FirstName(string)") End If End Sub 'A hashtable is used to return a type for the string value used in the header text. Private Sub FillTypeLookup() _typeLookup.Add("string", GetType([String])) _typeLookup.Add("byte", GetType([Byte])) _typeLookup.Add("boolean", GetType([Boolean])) _typeLookup.Add("datetime", GetType(DateTime)) _typeLookup.Add("decimal", GetType([Decimal])) _typeLookup.Add("double", GetType([Double])) _typeLookup.Add("int16", GetType(Int16)) _typeLookup.Add("int32", GetType(Int32)) _typeLookup.Add("int", GetType(Int32)) _typeLookup.Add("integer", GetType(Int32)) _typeLookup.Add("int64", GetType(Int64)) _typeLookup.Add("sbyte", GetType([SByte])) _typeLookup.Add("single", GetType([Single])) _typeLookup.Add("time", GetType(DateTime)) _typeLookup.Add("date", GetType(DateTime)) _typeLookup.Add("uint16", GetType(UInt16)) _typeLookup.Add("uint32", GetType(UInt32)) _typeLookup.Add("uint64", GetType(UInt64)) End Sub ' Returns a type based on the string value passed in from the header text string. If no match is found, ' a string type is returned. ' The fieldType parameter represents the String value from the header command text string. Private Function GetFieldTypeFromString(fieldType As String) As Type If _typeLookup.Contains(fieldType) Then Return TryCast(_typeLookup(fieldType), Type) End If Return GetType([String]) End Function ' Parses the first line in the passed-in command text string to create the field names and field data types. ' The field information is stored in a CsvColumn struct, and these column info items are stored ' in an ArrayList. The column name is also added to a hashtable for easy lookup later. ' The header parameter represents the header string that contains all the fields. ' Returns True if it can parse the header string; otherwise False. Private Function ParseHeader(header As String) As Boolean Dim fieldName As String Dim index As Integer = 0 If header.IndexOf("(") = -1 Then Return False End If Dim matches As MatchCollection = _rxHeaderRow.Matches(header) _columns = New Object(matches.Count - 1) {} For Each match As Match In matches fieldName = match.Groups("fieldName").Value Dim fieldType As Type = GetFieldTypeFromString(match.Groups("fieldType").Value) _columns.SetValue(New CsvColumn(fieldName, fieldType), index) _columnLookup.Add(fieldName, index) index += 1 Next Return True End Function ' Ensures that the header contains columns in the form of name(type) ' The line parameter represents the raw header line from the file to fix up. ' Returns a modified header with default types appended to column names. Private Shared Function AddDefaultTypeToHeader(line As String) As String Const ColumnWithDataTypeRegex As String = "[""]?\w+[\""]?\(.+\)" Dim columns As String() = line.Split(New String() {","}, StringSplitOptions.None) Dim ret As String = Nothing For Each column As String In columns If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(ret) Then ret += "," End If If Not Regex.Match(column, ColumnWithDataTypeRegex).Success Then ret += column + "(string)" Else ret += column End If Next Return ret End Function ' Parses a row of data using a regular expression and stores the information inside an object ' array that is the current row of data. ' If the row does not have the correct number of fields, an exception is raised. ' The dataRow parameter represents the String value representing a comma delimited data row. ' Returns True if it can parse the data string; otherwise False. Private Function ParseDataRow(dataRow As String) As Boolean Dim index As Integer = 0 Dim tempData As String() = _rxDataRow.Split(dataRow) _currentRow = New Object(tempData.Length - 1) {} If tempData.Length <> _columns.Length Then Dim [error] As String = String.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, _ "Invalid row ""{0}"". The row does not contain the same number of data columns as the table header definition.", dataRow) Throw New InvalidOperationException([error]) End If For i As Integer = 0 To tempData.Length - 1 Dim value As String = tempData(i) If value.Length > 1 Then If value.IndexOf(""""c, 0) = 0 AndAlso value.IndexOf(""""c, 1) = value.Length - 1 Then value = value.Substring(1, value.Length - 2) End If End If _currentRow.SetValue(ConvertValue(GetFieldType(index), value), index) index += 1 Next Return True End Function ' Coverts the string value coming from the command text to the appropriate data type, based on the field's type. ' This also checks a few string value rules to decide if a String.Empty of System.Data.DBNull needs to be returned. ' The type parameter represents the Type of the current column the data belongs to. ' The originalValue parameter represents the String value coming from the command text. ' Returns the object resulting from the converted string, based on the type. Private Function ConvertValue(type As Type, originalValue As String) As Object Dim fieldType As Type = type Dim invariantCulture As CultureInfo = CultureInfo.InvariantCulture Try If originalValue = """""" OrElse originalValue = " " Then Return String.Empty End If If originalValue = "" Then Return DBNull.Value End If If originalValue = "DBNull" Then Return DBNull.Value End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType([String])) Then Return originalValue.Trim() End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType(Int32)) Then Return Convert.ToInt32(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType([Boolean])) Then Return Convert.ToBoolean(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType(DateTime)) Then Return Convert.ToDateTime(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType([Decimal])) Then Return Convert.ToDecimal(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType([Double])) Then Return Convert.ToDouble(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType(Int16)) Then Return Convert.ToInt16(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType(Int64)) Then Return Convert.ToInt64(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType([Single])) Then Return Convert.ToSingle(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType([Byte])) Then Return Convert.ToByte(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType([SByte])) Then Return Convert.ToSByte(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType(UInt16)) Then Return Convert.ToUInt16(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType(UInt32)) Then Return Convert.ToUInt32(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If If fieldType.Equals(GetType(UInt64)) Then Return Convert.ToUInt64(originalValue, invariantCulture) End If Catch e As Exception Throw New InvalidOperationException(String.Format("Input value '{0}' could not be converted to the type '{1}'.", originalValue, type), e) End Try 'If no match is found return DBNull instead. Return DBNull.Value End Function #Region "IDataReader Members" ' Advances the CsvDataReader to the next record. ' Returns True if there are more rows; otherwise, False. Public Function Read() As Boolean Implements IDataReader.Read If _textReader.Peek() > -1 Then ParseDataRow(_textReader.ReadLine()) Else Return False End If Return True End Function #End Region #Region "IDisposable Members" ' Releases the resources used by the CsvDataReader. Public Sub Dispose() Implements IDisposable.Dispose Dispose(True) GC.SuppressFinalize(Me) End Sub Private Sub Dispose(disposing As Boolean) If disposing Then If _textReader IsNot Nothing Then _textReader.Close() End If End If _typeLookup = Nothing _columnLookup = Nothing _columns = Nothing _currentRow = Nothing End Sub ' Allows an Object to attempt to free resources and perform ' other cleanup operations before the Object is reclaimed by garbage collection. Protected Overrides Sub Finalize() Try Dispose(False) Finally MyBase.Finalize() End Try End Sub #End Region #Region "IDataRecord Members" ' Gets the number of columns in the current row. Public ReadOnly Property FieldCount() As Integer Implements IDataRecord.FieldCount Get Return _columns.Length End Get End Property ' The i parameter represents the index of the field to find. ' Returns the Type information corresponding to the type of Object that would be returned from GetValue. Public Function GetFieldType(i As Integer) As Type Implements IDataReader.GetFieldType If i > _columns.Length - 1 Then Return Nothing End If Return DirectCast(_columns.GetValue(i), CsvColumn).DataType End Function ' Gets the name for the field to find. ' The i parameter represents the index of the field to find. ' Returns the name of the field or an empty string (""), if there is no value to return. Public Function GetName(i As Integer) As String Implements IDataRecord.GetName If i > _columns.Length - 1 Then Return String.Empty End If Return DirectCast(_columns.GetValue(i), CsvColumn).FieldName End Function ' The name parameter represents the name of the field to find. ' Returns the index of the named field. Public Function GetOrdinal(name As String) As Integer Implements IDataRecord.GetOrdinal Dim value As Object = _columnLookup(name) If value Is Nothing Then Throw New IndexOutOfRangeException("name") End If Return CInt(value) End Function ' The i parameter represents the index of the field to find. ' Returns the Object which contains the value of the specified field. Public Function GetValue(i As Integer) As Object Implements IDataRecord.GetValue If i > _columns.Length - 1 Then Return Nothing End If Return _currentRow.GetValue(i) End Function Public Overridable Function GetData(fieldIndex As Integer) As IDataReader Implements IDataReader.GetData Throw New NotSupportedException() End Function #End Region End Class End NamespaceC# code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy Codeusing System; using System.Collections; using System.Globalization; using System.IO; using System.Text.RegularExpressions; using GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.Data; namespace CustomDataProvider.CSVDataProvider { // Provides an implementation of IDataReader for the .NET Framework CSV Data Provider. internal class CsvDataReader : IDataReader { //NOTE: HashcodeProvider and Comparer need to be case-insensitive since TypeNames are capitalized differently in places. //Otherwise data types end up as strings when using Int32 vs int32. private Hashtable _typeLookup = new Hashtable(StringComparer.Create(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, false)); private Hashtable _columnLookup = new Hashtable(); private object[] _columns; private TextReader _textReader; private object[] _currentRow; //The regular expressions are set to be pre-compiled to make it faster. Since we were concerned about //multi-threading, we made the properties read-only so no one can change any properties on these objects. private static readonly Regex _rxDataRow = new Regex(@",(?=(?:[^""]*""[^""]*"")*(?![^""]*""))", RegexOptions.Compiled); //Used to parse the data rows. private static readonly Regex _rxHeaderRow = new Regex(@"(?<fieldName>(\w*\s*)*)\((?<fieldType>\w*)\)", RegexOptions.Compiled); //Used to parse the header rows. // Creates a new instance of the CsvDataReader class. // The textReader parameter represents the TextReader to use to read the data. public CsvDataReader(TextReader textReader) { _textReader = textReader; ParseCommandText(); } // Parses the passed-in command text. private void ParseCommandText() { if (_textReader.Peek() == -1) return; //Command text is empty or at the end already. FillTypeLookup(); string header = _textReader.ReadLine(); header = AddDefaultTypeToHeader(header); if (!ParseHeader(header)) throw new InvalidOperationException( "Field names and types are not defined. The first line in the CommandText must contain the field names and data types. e.g FirstName(string)"); } //A hashtable is used to return a type for the string value used in the header text. private void FillTypeLookup() { _typeLookup.Add("string", typeof (String)); _typeLookup.Add("byte", typeof (Byte)); _typeLookup.Add("boolean", typeof (Boolean)); _typeLookup.Add("datetime", typeof (DateTime)); _typeLookup.Add("decimal", typeof (Decimal)); _typeLookup.Add("double", typeof (Double)); _typeLookup.Add("int16", typeof (Int16)); _typeLookup.Add("int32", typeof (Int32)); _typeLookup.Add("int", typeof (Int32)); _typeLookup.Add("integer", typeof (Int32)); _typeLookup.Add("int64", typeof (Int64)); _typeLookup.Add("sbyte", typeof (SByte)); _typeLookup.Add("single", typeof (Single)); _typeLookup.Add("time", typeof (DateTime)); _typeLookup.Add("date", typeof (DateTime)); _typeLookup.Add("uint16", typeof (UInt16)); _typeLookup.Add("uint32", typeof (UInt32)); _typeLookup.Add("uint64", typeof (UInt64)); } // Returns a type based on the string value passed in from the header text string. If no match is found, a string type is returned. // The fieldType parameter represents the String value from the header command text string. private Type GetFieldTypeFromString(string fieldType) { if (_typeLookup.Contains(fieldType)) return _typeLookup[fieldType] as Type; return typeof (String); } // Parses the first line in the passed-in command text string to create the field names and field data types. The field information // is stored in a CsvColumn struct, and these column info items are stored in an ArrayList. The column name is also added // to a hashtable for easy lookup later. // The header parameter represents the header string that contains all the fields. // Returns True if it can parse the header string; otherwise False. private bool ParseHeader(string header) { string fieldName; int index = 0; if (header.IndexOf("(") == -1) return false; MatchCollection matches = _rxHeaderRow.Matches(header); _columns = new object[matches.Count]; foreach (Match match in matches) { fieldName = match.Groups["fieldName"].Value; Type fieldType = GetFieldTypeFromString(match.Groups["fieldType"].Value); _columns.SetValue(new CsvColumn(fieldName, fieldType), index); _columnLookup.Add(fieldName, index); index++; } return true; } // Ensures that the header contains columns in the form of name(type) // The line parameter represents the raw header line from the file to fix up. // Returns a modified header with default types appended to column names. private static string AddDefaultTypeToHeader(string line) { const string ColumnWithDataTypeRegex = @"[""]?\w+[\""]?\(.+\)"; string[] columns = line.Split(new string[] { "," }, StringSplitOptions.None); string ret = null; foreach (string column in columns) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(ret)) ret += ","; if (!Regex.Match(column, ColumnWithDataTypeRegex).Success) { ret += column + "(string)"; } else { ret += column; } } return ret; } // Parses a row of data using a regular expression and stores the information inside an object array that is the current row of data. // If the row does not have the correct number of fields, an exception is raised. // The dataRow parameter represents the String value representing a comma delimited data row. // Returns True if it can parse the data string; otherwise False. private bool ParseDataRow(string dataRow) { int index = 0; string[] tempData = _rxDataRow.Split(dataRow); _currentRow = new object[tempData.Length]; if (tempData.Length != _columns.Length) { string error = string.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, "Invalid row \"{0}\". The row does not contain the same number of data columns as the table header definition.", dataRow); throw new InvalidOperationException(error); } for (int i = 0; i < tempData.Length; i++) { string value = tempData[i]; if (value.Length > 1) { if (value.IndexOf('"', 0) == 0 && value.IndexOf('"', 1) == value.Length - 1) value = value.Substring(1, value.Length - 2); } _currentRow.SetValue(ConvertValue(GetFieldType(index), value), index); index++; } return true; } // Coverts the string value coming from the command text to the appropriate data type, based on the field's type. // This also checks a few string value rules to decide if a String.Empty of System.Data.DBNull needs to be returned. // The type parameter represents the Type of the current column the data belongs to. // The originalValue parameter represents the String value coming from the command text. // Returns the object resulting from the converted string, based on the type. private object ConvertValue(Type type, string originalValue) { Type fieldType = type; CultureInfo invariantCulture = CultureInfo.InvariantCulture; try { if (originalValue == "\"\"" || originalValue == " ") return string.Empty; if (originalValue == "") return DBNull.Value; if (originalValue == "DBNull") return DBNull.Value; if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (String))) return originalValue.Trim(); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (Int32))) return Convert.ToInt32(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (Boolean))) return Convert.ToBoolean(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (DateTime))) return Convert.ToDateTime(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (Decimal))) return Convert.ToDecimal(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (Double))) return Convert.ToDouble(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (Int16))) return Convert.ToInt16(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (Int64))) return Convert.ToInt64(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (Single))) return Convert.ToSingle(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (Byte))) return Convert.ToByte(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (SByte))) return Convert.ToSByte(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (UInt16))) return Convert.ToUInt16(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (UInt32))) return Convert.ToUInt32(originalValue, invariantCulture); if (fieldType.Equals(typeof (UInt64))) return Convert.ToUInt64(originalValue, invariantCulture); } catch (Exception e) { throw new InvalidOperationException( string.Format("Input value '{0}' could not be converted to the type '{1}'.", originalValue, type), e); } //If no match is found return DBNull instead. return DBNull.Value; } #region IDataReader Members // Advances the CsvDataReader to the next record. // Returns True if there are more rows; otherwise, False. public bool Read() { if (_textReader.Peek() > -1) ParseDataRow(_textReader.ReadLine()); else return false; return true; } #endregion #region IDisposable Members // Releases the resources used by the CsvDataReader. public void Dispose() { Dispose(true); GC.SuppressFinalize(this); } private void Dispose(bool disposing) { if (disposing) { if (_textReader != null) _textReader.Close(); } _typeLookup = null; _columnLookup = null; _columns = null; _currentRow = null; } // Allows an Object to attempt to free resources and perform other cleanup operations before the Object is reclaimed by garbage collection. ~CsvDataReader() { Dispose(false); } #endregion #region IDataRecord Members // Gets the number of columns in the current row. public int FieldCount { get { return _columns.Length; } } // The i parameter represents the index of the field to find. // Returns the Type information corresponding to the type of Object that would be returned from GetValue. public Type GetFieldType(int i) { if (i > _columns.Length - 1) return null; return ((CsvColumn) _columns.GetValue(i)).DataType; } // Gets the name for the field to find. // The i parameter represents the index of the field to find. // Returns the name of the field or an empty string (""), if there is no value to return. public string GetName(int i) { if (i > _columns.Length - 1) return string.Empty; return ((CsvColumn) _columns.GetValue(i)).FieldName; } // The name parameter represents the name of the field to find. // Returns the index of the named field. public int GetOrdinal(string name) { object value = _columnLookup[name]; if (value == null) throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("name"); return (int) value; } // The i parameter represents the index of the field to find. // Returns the Object which contains the value of the specified field. public object GetValue(int i) { if (i > _columns.Length - 1) return null; return _currentRow.GetValue(i); } public virtual IDataReader GetData(int fieldIndex) { throw new NotSupportedException(); } #endregion } } - Right-click the CSVDataProvider folder and select Add, then Class, then name the class CsvCommand and add code like the following to replace the default stub in the class. (You can safely ignore the errors, as they will go away when you add the CsvConnection class.)
Visual Basic code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy CodeImports System Imports System.IO Imports GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.Data Namespace CSVDataProvider ' Provides the IDbCommand implementation for the .NET Framework CSV Data Provider. Public NotInheritable Class CsvCommand Implements IDbCommand Private _commandText As String Private _connection As IDbConnection Private _commandTimeout As Integer Private _commandType As CommandType ' Creates a new instance of the CsvCommand class. Public Sub New() Me.New(String.Empty) End Sub ' Creates a new instance of the CsvCommand class with command text. ' The commandText parameter represents the command text. Public Sub New(commandText As String) Me.New(commandText, Nothing) End Sub ' Creates a new instance of the CsvCommand class with command text and a CsvConnection. ' The commandText parameter represents the command text. ' The connection parameter represents a CsvConnection to a data source. Public Sub New(commandText As String, connection As CsvConnection) _commandText = commandText _connection = connection End Sub ' Gets or sets the command to execute at the data source. Public Property CommandText() As String Implements IDbCommand.CommandText Get Return _commandText End Get Set(value As String) _commandText = value End Set End Property ' Gets or sets the wait time before terminating an attempt to execute the command and generating an error. Public Property CommandTimeout() As Integer Implements IDbCommand.CommandTimeout Get Return _commandTimeout End Get Set(value As Integer) _commandTimeout = value End Set End Property ' Gets or sets a value indicating how the CommandText property is interpreted. ' Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. Public Property CommandType() As CommandType Implements IDbCommand.CommandType Get Return _commandType End Get Set(value As CommandType) _commandType = value End Set End Property ' Gets or sets the CsvConnection used by this instance of the CsvCommand. Public Property Connection() As IDbConnection Get Return _connection End Get Set(value As IDbConnection) _connection = value End Set End Property ' Sends the CommandText to the CsvConnection, and builds a CsvDataReader using one of the CommandBehavior values. ' The behavior parameter represents a CommandBehavior value. ' Returns a CsvDataReader object. Public Function ExecuteReader(behavior As CommandBehavior) As IDataReader Implements IDbCommand.ExecuteReader Return New CsvDataReader(New StreamReader(_commandText)) End Function ' Returns a string that represents the command text with the parameters expanded into constants. Public Function GenerateRewrittenCommandText() As String Implements IDbCommand.GenerateRewrittenCommandText Return _commandText End Function ' Sends the CommandText to the CsvConnection and builds a CsvDataReader. ' Returns a CsvDataReader object. Public Function ExecuteReader() As IDataReader Implements IDbCommand.ExecuteReader Return ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.SchemaOnly) End Function #Region "Non implemented IDbCommand Members" Public ReadOnly Property Parameters() As IDataParameterCollection Implements IDbCommand.Parameters Get Throw New NotImplementedException() End Get End Property Public Property Transaction() As IDbTransaction Implements IDbCommand.Transaction Get Throw New NotImplementedException() End Get Set(value As IDbTransaction) Throw New NotImplementedException() End Set End Property Public Sub Cancel() Implements IDbCommand.Cancel End Sub Public Function CreateParameter() As IDataParameter Implements IDbCommand.CreateParameter Throw New NotImplementedException() End Function #End Region #Region "IDisposable Members" ' Releases the resources used by the CsvCommand. Public Sub Dispose() Implements IDisposable.Dispose Dispose(True) GC.SuppressFinalize(Me) End Sub Private Sub Dispose(disposing As Boolean) If disposing Then If _connection IsNot Nothing Then _connection.Dispose() _connection = Nothing End If End If End Sub #End Region End Class End NamespaceC# code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy Codeusing System; using System.IO; using GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.Data; namespace CustomDataProvider.CSVDataProvider { // Provides the IDbCommand implementation for the .NET Framework CSV Data Provider. public sealed class CsvCommand : IDbCommand { private string _commandText; private IDbConnection _connection; private int _commandTimeout; private CommandType _commandType; /// Creates a new instance of the CsvCommand class. public CsvCommand() : this(string.Empty) { } // Creates a new instance of the CsvCommand class with command text. // The commandText parameter represents the command text. public CsvCommand(string commandText) : this(commandText, null) { } // Creates a new instance of the CsvCommand class with command text and a CsvConnection. // The commandText parameter represents the command text. // The connection parameter represents a CsvConnection to a data source.? public CsvCommand(string commandText, CsvConnection connection) { _commandText = commandText; _connection = connection; } // Gets or sets the command to execute at the data source. public string CommandText { get { return _commandText; } set { _commandText = value; } } // Gets or sets the wait time before terminating an attempt to execute the command and generating an error. public int CommandTimeout { get { return _commandTimeout; } set { _commandTimeout = value; } } // Gets or sets a value indicating how the CommandText property is interpreted. // Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. public CommandType CommandType { get { return _commandType; } set { _commandType = value; } } // Gets or sets the CsvConnection used by this instance of the CsvCommand. public IDbConnection Connection { get { return _connection; } set { _connection = value; } } // Sends the CommandText to the CsvConnection, and builds a CsvDataReader using one of the CommandBehavior values. // The behavior parameter represents a CommandBehavior value. // Returns a CsvDataReader object. public IDataReader ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior behavior) { return new CsvDataReader(new StreamReader(_commandText)); } // Returns a string that represents the command text with the parameters expanded into constants. public string GenerateRewrittenCommandText() { return _commandText; } // Sends the CommandText to the CsvConnection and builds a CsvDataReader. // Returns a CsvDataReader object. public IDataReader ExecuteReader() { return ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.SchemaOnly); } #region Non implemented IDbCommand Members public IDataParameterCollection Parameters { get { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } public IDbTransaction Transaction { get { throw new NotImplementedException(); } set { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } public void Cancel() { } public IDataParameter CreateParameter() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } #endregion #region IDisposable Members // Releases the resources used by the CsvCommand. public void Dispose() { Dispose(true); GC.SuppressFinalize(this); } private void Dispose(bool disposing) { if (disposing) { if (_connection != null) { _connection.Dispose(); _connection = null; } } } #endregion } } - Right-click the CSVDataProvider folder and select Add, then Class, then name the class CsvConnection and add code like the following to replace the default stub in the class.
Visual Basic code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy CodeImports System Imports System.Collections.Specialized Imports GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.Data Namespace CSVDataProvider ' Provides an implementation of IDbConnection for the .NET Framework CSV Data Provider. Public NotInheritable Class CsvConnection Implements IDbConnection Private _localizedName As String ' Creates a new instance of the CsvConnection class. Public Sub New() _localizedName = "Csv" End Sub ' Creates a new instance of the CsvConnection class. ' The localizedName parameter represents the localized name for the CsvConnection instance. Public Sub New(localizeName As String) _localizedName = localizeName End Sub #Region "IDbConnection Members" ' Gets or sets the string used to open the connection to the data source. ' Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. Public Property ConnectionString() As String Implements IDbConnection.ConnectionString Get Return String.Empty End Get Set(value As String) End Set End Property ' Gets the amount of time to wait while trying to establish a connection before terminating ' the attempt and generating an error. ' Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. Public ReadOnly Property ConnectionTimeout() As Integer Implements IDbConnection.ConnectionTimeout Get Throw New NotImplementedException() End Get End Property ' Begins a data source transaction. ' Returns an object representing the new transaction. ' Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. Public Function BeginTransaction() As IDbTransaction Implements IDbConnection.BeginTransaction Return Nothing End Function ' Opens a data source connection. ' Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. Public Sub Open() Implements IDbConnection.Open End Sub ' Closes the connection to the data source. This is the preferred method of closing any open connection. Public Sub Close() Implements IDbConnection.Close Dispose() End Sub ' Creates and returns a CsvCommand object associated with the CsvConnection. Public Function CreateCommand() As IDbCommand Implements IDbConnection.CreateCommand Return New CsvCommand(String.Empty) End Function Public Property DataProviderService() As IDataProviderService Implements IDbConnection.DataProviderService Get Return Nothing End Get Set(value As IDataProviderService) End Set End Property #End Region #Region "IDisposable Members" ' Releases the resources used by the CsvConnection. Public Sub Dispose() Implements IDisposable.Dispose Dispose(True) GC.SuppressFinalize(Me) End Sub Private Sub Dispose(disposing As Boolean) End Sub ' Allows an Object to attempt to free resources and perform other cleanup operations ' before the Object is reclaimed by garbage collection. Protected Overrides Sub Finalize() Try Dispose(False) Finally MyBase.Finalize() End Try End Sub #End Region #Region "IExtension Members" ' Gets the localized name of the CsvConnection. Public ReadOnly Property LocalizedName() As String Implements IDbConnection.LocalizedName Get Return _localizedName End Get End Property ' Specifies any configuration information for this extension. ' The configurationSettings parameter represents a NameValueCollection of the settings. Public Sub SetConfiguration(configurationSettings As NameValueCollection) Implements IDbConnection.SetConfiguration End Sub #End Region End Class End NamespaceC# code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy Codeusing System; using System.Collections.Specialized; using GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.Data; namespace CustomDataProvider.CSVDataProvider { // Provides an implementation of IDbConnection for the .NET Framework CSV Data Provider. public sealed class CsvConnection : IDbConnection { private string _localizedName; / Creates a new instance of the CsvConnection class. public CsvConnection() { _localizedName = "Csv"; } // Creates a new instance of the CsvConnection class. // The localizedName parameter represents the localized name for the CsvConnection instance. public CsvConnection(string localizeName) { _localizedName = localizeName; } #region IDbConnection Members // Gets or sets the string used to open the connection to the data source. // Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. public string ConnectionString { get { return string.Empty; } set { ; } } // Gets the amount of time to wait while trying to establish a connection before terminating the attempt and generating an error. // Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. public int ConnectionTimeout { get { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } // Begins a data source transaction. // Returns an object representing the new transaction. // Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. public IDbTransaction BeginTransaction() { return null; } // Opens a data source connection. // Remarks: We don't use this one for the Csv Data Provider. public void Open() { ; } // Closes the connection to the data source. This is the preferred method of closing any open connection. public void Close() { Dispose(); } // Creates and returns a CsvCommand object associated with the CsvConnection. public IDbCommand CreateCommand() { return new CsvCommand(string.Empty); } public IDataProviderService DataProviderService { get { return null; } set { } } #endregion #region IDisposable Members // Releases the resources used by the CsvConnection. public void Dispose() { Dispose(true); GC.SuppressFinalize(this); } private void Dispose(bool disposing) { } // Allows an Object to attempt to free resources and perform other cleanup operations before the Object is reclaimed by garbage collection. ~CsvConnection() { Dispose(false); } #endregion #region IExtension Members // Gets the localized name of the CsvConnection. public string LocalizedName { get { return _localizedName; } } // Specifies any configuration information for this extension. // The configurationSettings parameter represents a NameValueCollection of the settings. public void SetConfiguration(NameValueCollection configurationSettings) { } #endregion } } - Right-click the CSVDataProvider folder and select Add, then Class, then name the class CsvDataProviderFactory and add code like the following to replace the default stub in the class.
Visual Basic code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy CodeImports GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.Data Imports GrapeCity.BI.Data.DataProviders Namespace CSVDataProvider ' Implements the DataProviderFactory for .NET Framework CSV Data Provider. Public Class CsvDataProviderFactory Inherits DataProviderFactory ' Creates new instance of the CsvDataProviderFactory class. Public Sub New() End Sub ' Returns a new instance of the the CsvCommand. Public Overrides Function CreateCommand() As IDbCommand Return New CsvCommand() End Function ' Returns a new instance of the the CsvConnection. Public Overrides Function CreateConnection() As IDbConnection Return New CsvConnection() End Function End Class End NamespaceC# code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy Codeusing GrapeCity.ActiveReports.Extensibility.Data; using GrapeCity.BI.Data.DataProviders; namespace CustomDataProvider.CSVDataProvider { // Implements the DataProviderFactory for .NET Framework CSV Data Provider. public class CsvDataProviderFactory : DataProviderFactory { // Creates new instance of the CsvDataProviderFactory class. public CsvDataProviderFactory() { } // Returns a new instance of the the CsvCommand. public override IDbCommand CreateCommand() { return new CsvCommand(); } // Returns a new instance of the the CsvConnection. public override IDbConnection CreateConnection() { return new CsvConnection(); } } }
 To add a button to the query editor
To add a button to the query editor
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click the CSVDataProvider folder and select Add, then Class, then name the class QueryEditor and add code like the following to replace the default stub in the class.
Visual Basic code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy CodeImports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Drawing.Design
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Linq
Imports System.Text
Imports System.Text.RegularExpressions
Imports System.Windows.Forms
Imports System.Windows.Forms.DesignNamespace CSVDataProvider
Public NotInheritable Class QueryEditor
Inherits UITypeEditor
Dim path = ""
Friend WithEvents btn As New Button()
Public Overrides Function GetEditStyle(context As System.ComponentModel.ITypeDescriptorContext) As UITypeEditorEditStyle
Return UITypeEditorEditStyle.DropDown
End FunctionPublic Overrides Function EditValue(context As System.ComponentModel.ITypeDescriptorContext, provider As System.IServiceProvider, value As Object) As Object
Dim edSvc As IWindowsFormsEditorService = DirectCast(provider.GetService(GetType(IWindowsFormsEditorService)), IWindowsFormsEditorService)
btn.Text = "Select CSV File..."
Dim pdg = btn.Padding
pdg.Bottom += 2
btn.Padding = pdgedSvc.DropDownControl(btn)
If String.IsNullOrEmpty(path) Then
Return String.Empty
End If
If Not File.Exists(path) Then
Return String.Empty
End IfReturn path
End Function
Private Sub btn_Click(sender As System.Object, e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn.Click
Using openDlg = New OpenFileDialog()
openDlg.Filter = "CSV Files (*.csv)|*.csv|All Files (*.*)|*.*"
If openDlg.ShowDialog() <> DialogResult.OK Then
path = ""
Else
path = openDlg.FileName
End If
End Using
End SubEnd Class
End Namespace
C# code. Paste it to replace the default stub in the class.  Copy Code
Copy Codeusing System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Drawing.Design; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Text.RegularExpressions; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Windows.Forms.Design; namespace CustomDataProvider.CSVDataProvider { public sealed class QueryEditor : UITypeEditor { public override UITypeEditorEditStyle GetEditStyle(System.ComponentModel.ITypeDescriptorContext context) { return UITypeEditorEditStyle.DropDown; } public override object EditValue(System.ComponentModel.ITypeDescriptorContext context, System.IServiceProvider provider, object value) { IWindowsFormsEditorService edSvc = (IWindowsFormsEditorService)provider.GetService(typeof(IWindowsFormsEditorService)); var path = ""; var btn = new Button(); btn.Text = "Select CSV File..."; var pdg = btn.Padding; pdg.Bottom += 2; btn.Padding = pdg; btn.Click += delegate { using (var openDlg = new OpenFileDialog()) { openDlg.Filter = "CSV Files (*.csv)|*.csv|All Files (*.*)|*.*"; if (openDlg.ShowDialog() != DialogResult.OK) path = ""; else path = openDlg.FileName; } }; edSvc.DropDownControl(btn); if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(path)) return string.Empty; if (!File.Exists(path)) return string.Empty; return path; } } } - In the Solution Explorer, right-click the CustomDataProviderDemo project and select Add Reference. In the Add Reference dialog that appears, on the Projects tab, select CustomDataProvider and click OK.
- Run the project, and follow the instructions in the RichTextBox to see the custom data provider in action.



 Hide All
Hide All