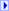
Color scales are visual guides that help you understand data distribution and variation. A two-color scale compares a range of cells by using a gradation of two colors. The shade of the color represents higher or lower values. For example, in a green and red color scale, you can specify that higher value cells are closer to a green color and lower value cells are closer to a red color. You can specify the value type, value, and color for the minimum and maximum properties.
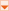
A three-color scale compares a range of cells by using a gradation of three colors. The shade of the color represents higher, middle, or lower values. For example, in a green, yellow, and red color scale, you can specify that higher value cells have a green color, middle value cells have a yellow color, and lower value cells have a red color. You can specify the value type, value, and color for the minimum, middle, and maximum properties.
The following image uses the three color rule:
Using Code
Set the properties of the TwoColorScaleConditionalFormattingRule class or the ThreeColorScaleConditionalFormattingRule class and then apply the formatting.
Example
This example code creates a three color rule and uses the SetConditionalFormatting method to apply the rule.
| C# |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
|
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) } |
|
| VB |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
|
Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click End Sub |
|
Using the Spread Designer
- In the work area, select the cell or cells for which you want to set the conditional format.
- Under the Home menu, select the Conditional Formatting icon in the Style section, then select the Color Scales option, and then choose the color set.
- From the File menu choose Apply and Exit to apply your changes to the component and exit Spread Designer.